Ensuring effective cement placement is essential for long-term well integrity. One of the main performance indicators in any cementing operation is displacement efficiency, or how completely drilling fluid is replaced by cement slurry. Small inefficiencies can leave behind residual mud, reducing zonal isolation and potentially compromising the well. To improve predictability and design accuracy, engineers continue to explore how numerical modeling can mirror real-world results.
Understanding the Role of Advanced Modeling
High-resolution simulation tools allow engineers to study fluid flow behavior within the annulus under complex well geometries. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD), often implemented through models like ANSYS, provides detailed insights into velocity distribution, turbulence, and potential areas of poor displacement. While powerful, these methods can be computationally demanding—making them less practical for frequent use during cementing design.
A Study in Comparison
To evaluate the performance of more efficient modeling approaches, a comparative study was conducted examining three data sources:
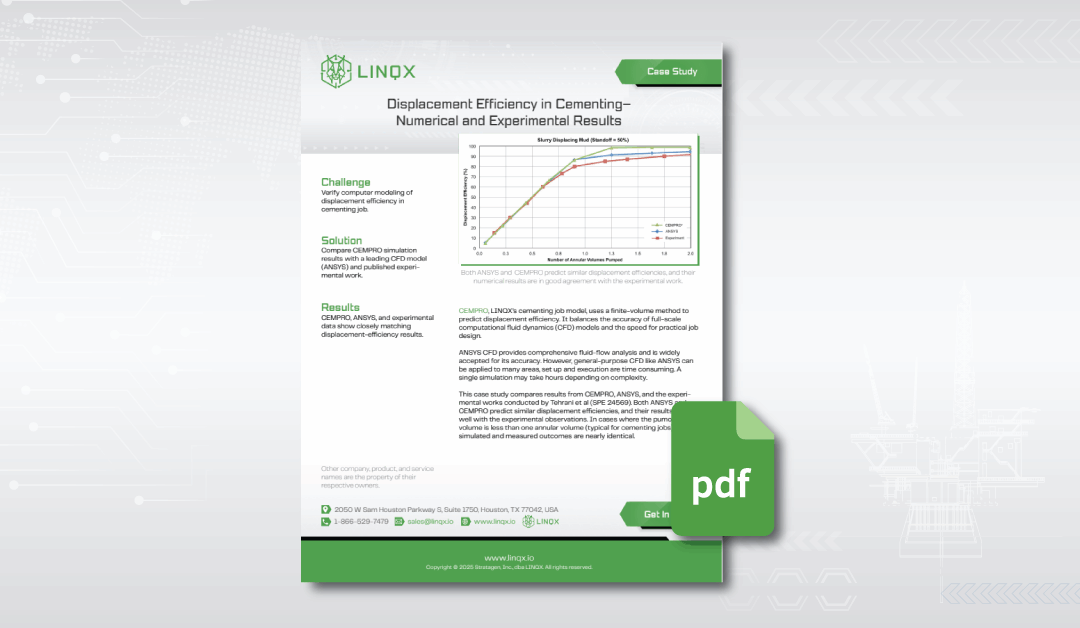
- Experimental measurements reported by Tehrani et al. (SPE 24569)
- High-fidelity CFD modeling using ANSYS
- Finite-volume numerical modeling developed specifically for cementing analysis
The test case focused on conditions with 50% standoff, representing a realistic and challenging geometry often encountered in deviated wells. Each method was used to calculate displacement efficiency across varying annular volumes pumped.
See our case study for more detail on numerical and experimental comparisons
Findings and Correlation
The study revealed close agreement between all three approaches. Both numerical models—CFD and finite-volume—captured the experimental displacement trends with high consistency. For cases where less than one annular volume was pumped, the predicted and measured efficiencies were nearly identical. This alignment demonstrates that finite-volume modeling can replicate the accuracy of CFD while offering a faster, more accessible solution for engineers.
Practical Implications for Cementing Engineers
Validated modeling tools help engineers move beyond trial-and-error design. By accurately representing fluid interaction and displacement dynamics, these models can support:
- Faster scenario evaluation during pre-job planning
- Improved prediction of flow channeling and mud removal
- More confident optimization of pumping schedules and flow rates
Such methods provide a dependable foundation for balancing operational efficiency with well integrity.
From Validation to Application
Building on the results of this comparative study, CEMPRO applies the same finite-volume approach to practical cementing design. It enables engineers to simulate displacement efficiency quickly and reliably, offering insight comparable to CFD without the computational burden. See how we do it. Contact us to learn more.